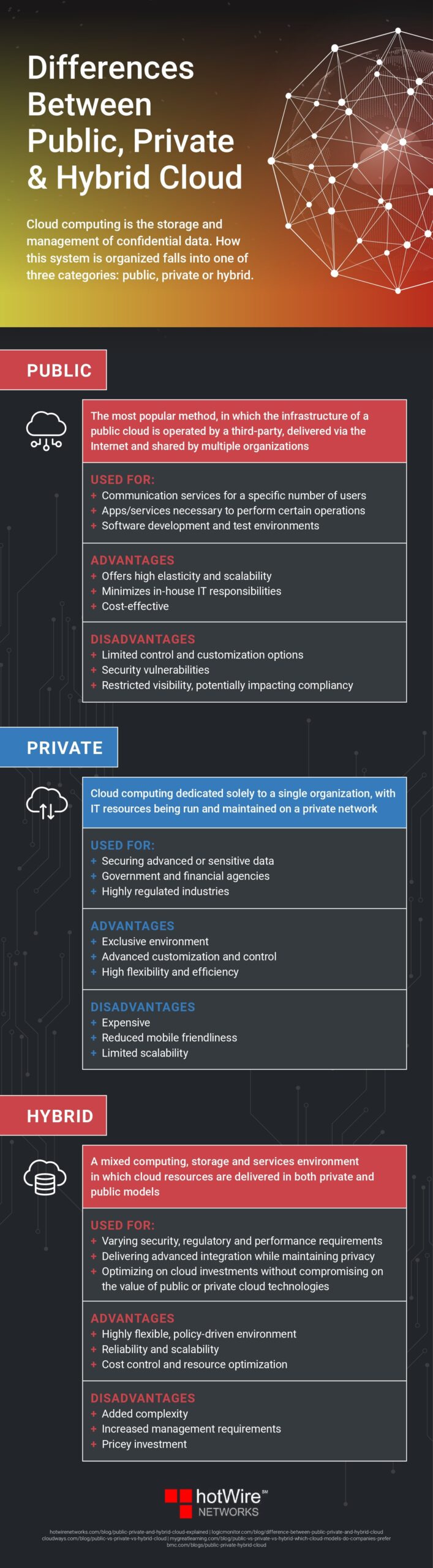
Cloud computing is categorized into three main types: public, private, and hybrid, each with distinct features and applications.
Public Cloud: This popular option is managed by third-party providers and accessible via the internet, serving multiple organizations. It is suitable for communication services, operational apps, and software development and testing. Public clouds offer elasticity, scalability, and cost-effectiveness but come with limited control, security concerns, and compliance challenges.
Private Cloud: Exclusively dedicated to a single organization, private clouds run on a private network. They excel in securing sensitive data, making them ideal for government, financial agencies, and regulated industries. Private clouds offer advanced customization and control but can be expensive and less mobile-friendly.
Hybrid Cloud: Hybrid environments combine private and public cloud resources, catering to varying security, regulatory, and performance needs. They optimize cloud investments while maintaining privacy, providing flexibility, scalability, and cost control. However, they require complex management and significant investment.
Choosing the right cloud model depends on an organization’s specific requirements and priorities. If you are interested in learning more about the advantages and disadvantages to each, check out the resource below.
Infographic created by Hotwire Networks

 How To Incorporate Sustainability At Your Next Business Event
How To Incorporate Sustainability At Your Next Business Event